In this blog post, we’ll explore a real-world scenario where we need to migrate and replicate data between an EC2-hosted MySQL database and Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) MySQL instance. This setup is critical for maintaining data integrity, ensuring high availability, and facilitating seamless scalability in a production environment.
Scenario Overview
Imagine you have an existing MySQL database running on an EC2 instance that handles live traffic for your application. To improve scalability and reduce operational overhead, you decide to migrate this database to Amazon RDS while setting up replication to keep both databases synchronized. This ensures minimal downtime and data consistency during the migration process.
Prerequisites
- Access to an EC2 instance with MySQL installed.
- Access to an RDS MySQL instance.
- Basic understanding of MySQL administration and AWS services.
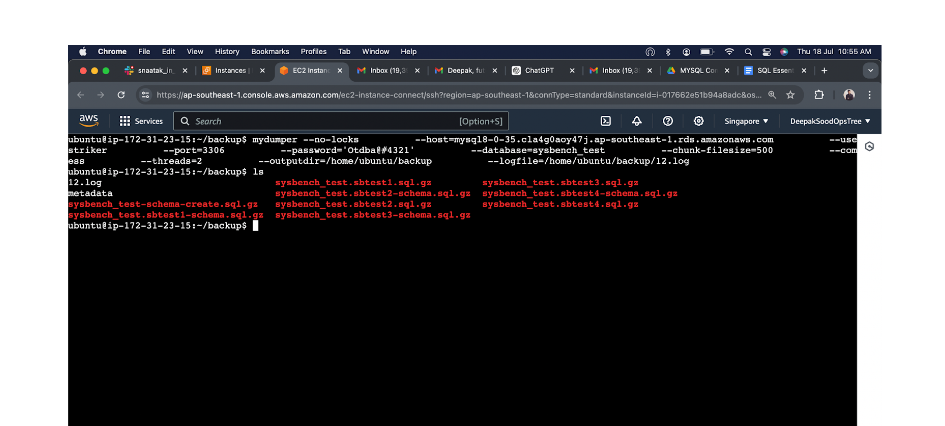
Part 1: Taking Backup from EC2 MySQL Using MyDumper
- Commands to take a backup of your MySQL database using MyDumper.
- Example command:
mydumper --no-locks --host=<HOST> --user=<USERNAME> --port=<PORT> --password='<PASSWORD>' --database=<DATABASE> --chunk-filesize=<CHUNK_SIZE> --compress --threads=<THREADS> --outputdir=<OUTPUT_DIR> --logfile=<LOGFILE>
 Part 2: Restore Backup to RDS MySQL Using MyLoader
Part 2: Restore Backup to RDS MySQL Using MyLoader
- Prepare RDS MySQL Instance for Restore.
- Example command:
myloader --host=<HOST> --compress-protocol --queries-per-transaction=<QUERIES_PER_TRANSACTION> --user=<USERNAME> --port=<PORT> --password='<PASSWORD>' --source-db=<SOURCE_DATABASE> --database=<TARGET_DATABASE> --threads=<THREADS> --directory=<DIRECTORY>
Part 3: Setting Up Replication Between EC2 MySQL and RDS MySQL
- Create Replication User: Create a user specifically for replication on EC2 MYSQL.
CREATE USER 'repl_user’@‘%’ IDENTIFIED BY 'Repl@#3421';
- Grant Replication Permissions: Grant the necessary permissions to the replication user. The user needs the REPLICATION SLAVE privilege to connect and replicate data.
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'repl_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
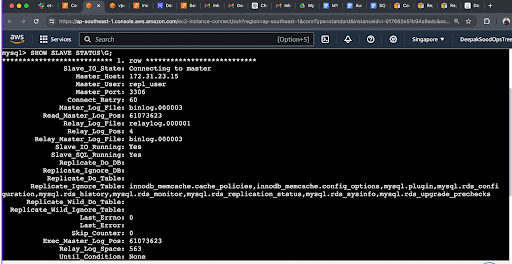
Part4: Configure RDS MySQL as Slave
- On your RDS MySQL instance, configure it as a slave to replicate data from the EC2 MySQL master.
- Use mysql.rds_set_external_master procedure to set up replication parameters:
CALL mysql.rds_set_external_master('<EC2_IP>', <port>, '<replication_user>', '<password>', '<binlog_file>', <binlog_position>, 0);
START SLAVE;
SHOW SLAVE STATUS \G;
Blog Pundits: Deepak Sood and Sandeep Rawat
OpsTree is an End-to-End DevOps Solution Provider.
Connect with Us
