Imagine starting a new coding project, but you have no folder structure-
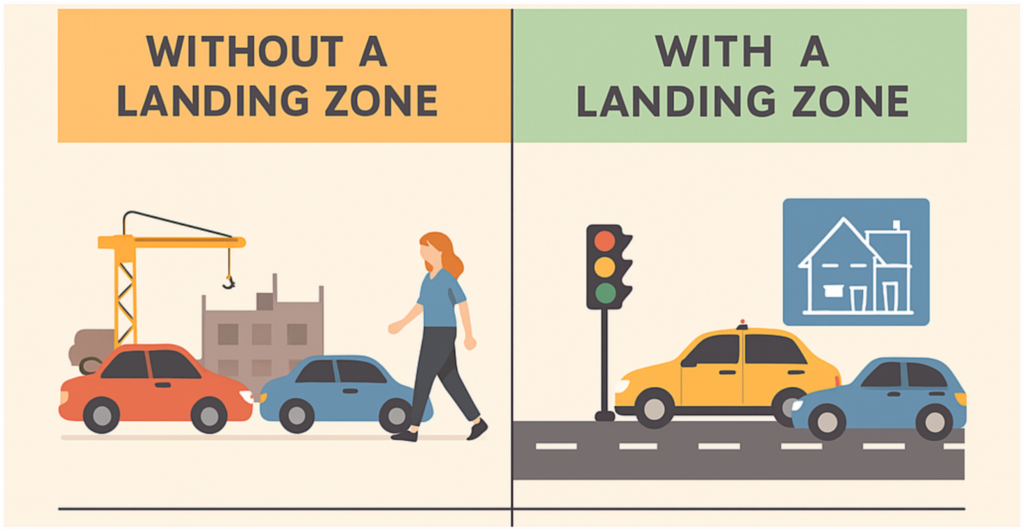
What is Landing Zone?
In simple terms, a Cloud Landing Zone helps you set up GCP environments using standard configurations so you can quickly and securely start your GCP journey without confusion.
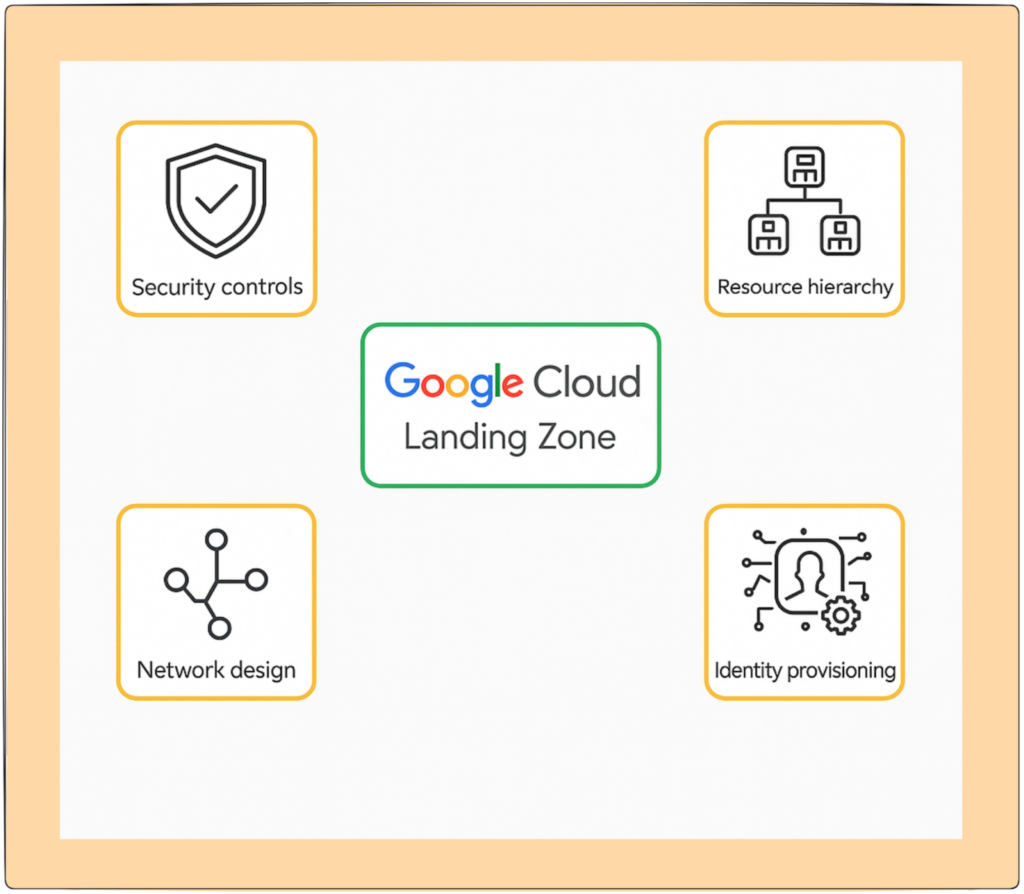
Security Controls – Ensure proper IAM policies, encryption, and compliance to protect cloud resources.
Resource Hierarchy – Organizes projects, folders, and resources for better management and governance.
Network Design – Sets up VPCs, subnets, and firewall rules to maintain a secure and scalable network.
Identity Provisioning – Manages user access, roles, and authentication to control who can do what in the cloud.
Problem Solved by Landing Zone

| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Unstructured Cloud Setup | Provides a predefined framework for resources and governance. |
| Security Gaps & Access Issues | Enforces IAM, encryption, and security policies for protection. |
| Uncontrolled Costs | Implements budget controls and monitoring to prevent overspending. |
| Inconsistent Networking | Sets up standardized VPCs, subnets, and firewall rules. |
| Compliance & Governance Challenges | Aligns cloud setup with security and compliance standards. |
| Lack of Visibility & Monitoring |
Enables centralized logging, monitoring,
and alerting for better management. |
Architecture
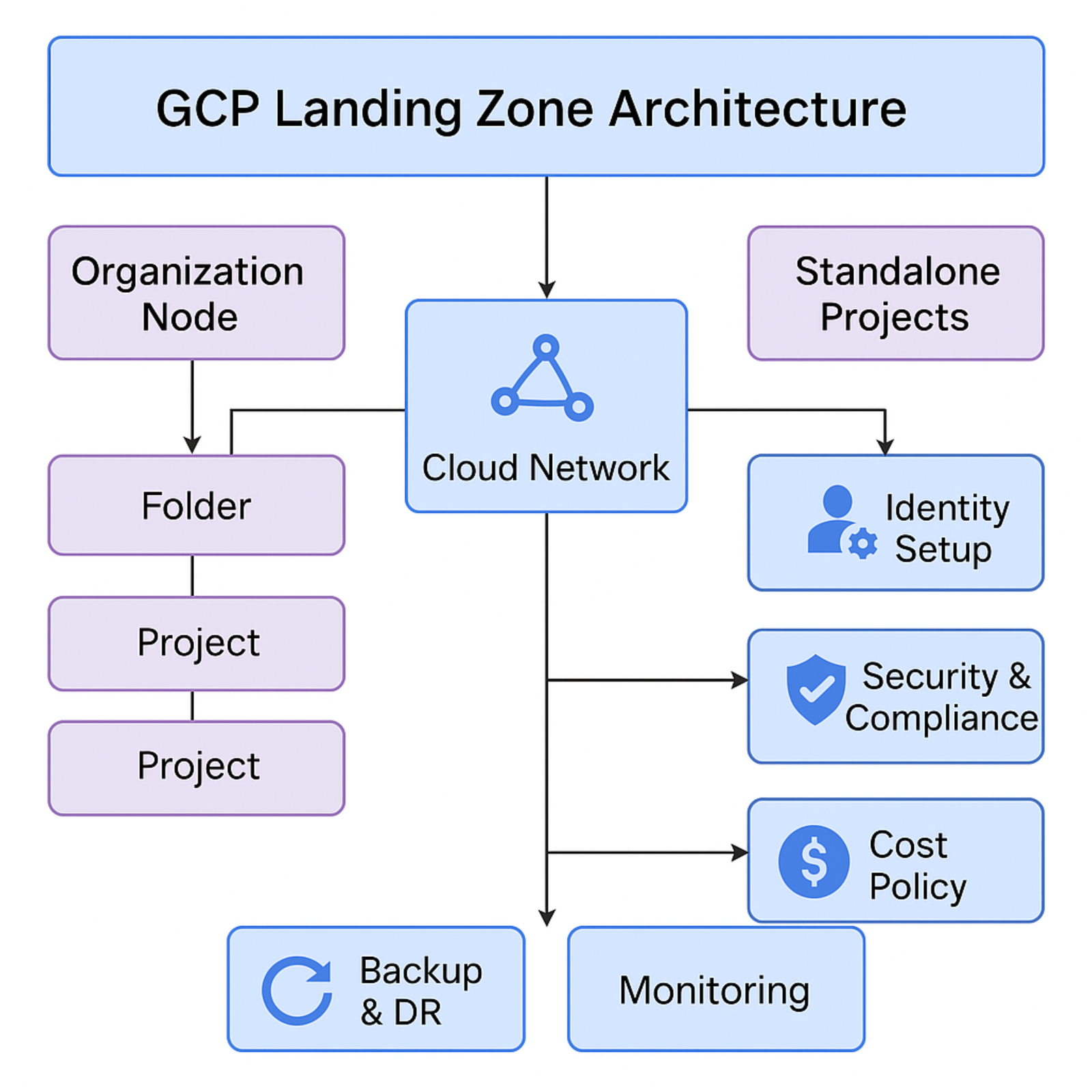
| Component | Description | Purpose in Landing Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Organization Node | The root entity in Google Cloud that manages all resources under a single structure. | Ensures centralized governance and policy enforcement. |
| Folder | Logical grouping of projects based on business units, environments, or applications. |
Helps in managing access controls, billing, and compliance. |
| Project | Individual resource containers where workloads run. |
Provides isolation for applications, services, and teams. |
| Cloud Network | The core networking infrastructure connects all projects. |
Ensures secure, scalable, and organized communication between resources. |
| Standalone Projects | Independent projects that do not belong to a structured folder hierarchy. | Useful for isolated workloads or experiments without affecting the enterprise setup. |
| Identity Setup | Manages user authentication and access controls (IAM). | Enforces least privilege access and protects cloud resources. |
| Security & Compliance |
Includes policies, encryption, and firewall rules. | Ensures compliance with organizational and regulatory security standards. |
| Cost Policy | Implements budget tracking and cost optimization strategies. | Prevents unexpected expenses and ensures financial control. |
| Backup & DR | Backup and disaster recovery mechanisms for data protection. | Ensures business continuity and data recovery in case of failures. |
| Monitoring | Tracks performance, logs security events, and enables alerting. | Helps in proactive issue detection and resolution. |
Case Study: ADEO’s Internal Platform for Faster Provisioning
- Challenge:
ADEO, a company in the process of migrating to the cloud, needed a way to automate processes and easily deploy customized configurations, especially for legacy applications requiring internal private network connectivity between APIs. - Solution:
ADEO built an internal platform, which they call the Landing Zone on Google Cloud, to automate processes and deploy customized configurations.
Conclusion
This blog explored the importance of a GCP Landing Zone and how it helps organizations build a secure, well-structured, and scalable cloud environment. We discussed the key pillars of a Landing Zone, the challenges it solves, and its architectural design. By implementing a Landing Zone, businesses can enhance security, streamline operations, control costs, and ensure compliance from the start. Thanks for reading. I’d appreciate your feedback. Please leave a comment below if you have any suggestions or questions.
