Table of Contents
Introduction and Overview
1. Purpose and Scope
The purpose of this High-Level Design (HLD) document is to provide a comprehensive, non-technical overview of the Hoop.dev solution, an access gateway designed to secure and streamline developer access to critical infrastructure (databases and servers).
The scope covers the core architectural components, key features, data flow, and deployment models of the Hoop platform.
2. The Business Problem
Organizations currently face major challenges in managing infrastructure access:
- Security Risks: Overly permissive access policies and reliance on shared credentials.
- Productivity Bottlenecks: Complex, manual “break-glass” approval workflows for infrastructure access.
- Compliance and Audit: Inadequate, non-standardized audit trails and visibility gaps.
- Data Exposure: Risks associated with developers accessing sensitive data (PII, credentials) directly in production environments.
3. The Proposed Solution
Hoop.dev is a centralized access gateway that acts as a secure intermediary between users and infrastructure. It delivers zero-config security and AI-powered automations to protect resources while providing secure, auditable, and easy-to-manage access.
The solution enables a shift from static, permanent access to dynamic, temporary, and auditable session-based access.

Get enterprise-grade data engineering solutions to unlock advanced analytics and AI readiness
Solution Requirements
1. Functional Requirements (What the system must do)
| ID | Requirement Description | Hoop Feature Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| FR1 | Provide secure, authenticated gateway access to various infrastructure types (Databases, SSH Servers, Web Applications, Cloud Services). |
Connections, Clients (Web App / CLI) |
| FR2 | Automatically mask sensitive data in real-time at the protocol layer. | AI Data Masking |
| FR3 | Enforce granular access policies based on user/group identity for specific connections. |
Access Control |
| FR4 | Enable time-based access session requests requiring an explicit review and approval workflow. |
Reviews |
| FR5 | Prevent high-risk operations or command execution in real time. | Guardrails (Intelligent Command Filtering) |
| FR6 | Allow secure, templated, and auditable execution of operational procedures (for example, automated fixes). |
Runbooks (Git-based) |
| FR7 | Integrate with existing Secrets Management tools to dynamically inject credentials into sessions without exposing them to users. |
Secrets Management |
2 . Non-Functional Requirements (How well the system must perform)
| Category | Requirement Description |
|---|---|
| Security | Zero-config DLP policies, identity provider integration, session authentication, and command-level filtering must be enforced in real-time. |
| Auditability | All access sessions, commands executed, and data flows must be fully recorded and logged (Session Recording). |
| Performance | The gateway must introduce minimal latency when proxying access traffic between the user and the target infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Must support both Managed Service and Self-Hosted deployments (Docker, Kubernetes) to handle varying organizational sizes and load. |
| Compliance | Must provide logs and session records suitable for meeting regulatory audit requirements (e.g., GDPR, SOC 2). |
High-Level Solution Architecture
1. System Context Diagram
The Hoop platform sits as a centralized proxy between users/approvers and all protected infrastructure.
2. Logical Breakdown and Major Components
The Hoop platform is composed of several high-level services:
| Component | Description | Key Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Hoop Gateway Core | The main access proxy service. All traffic from clients to infrastructure flows through here. | Session management, Protocol handling, Traffic forwarding |
| Policy & Guardrails Engine | A real-time processing layer that enforces access policies and command filtering. | Access Control (FR3), Guardrails (FR5), Session Review Check (FR4) |
| Data Masking Engine | A protocol-aware layer that inspects and transforms data streams in transit. | AI Data Masking (FR2) on request and response data |
| Audit & Logging Module | Captures and stores comprehensive records of all activity. | Session Recording, Auditing (NFR – Auditability) |
| Runbook Execution Service | Manages the execution lifecycle of automated Git-based runbooks. | Securely executes pre-defined procedures (FR6) |
| Integration Layer | Handles communication with external organizational services. | Connects to IdPs (Okta, Azure AD), Secrets Managers (HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager), and Ticketing/Approval systems (Slack, Jira) |
| Client Interface | The primary means by which users interact with Hoop. | Web App, Command Line Interface (CLI) |
Data Flow and Use Cases
1. Use Case: Secure VM Access with Approval (Reviews)
This sequence describes a developer securely accessing a production VM through Hoop with an approval workflow.
1. Request:
A Developer uses the Hoop CLI or Hoop Web App to request temporary SSH access to a production VM (e.g. dev-ashwathama-app-sonarqube-cloud-ops-crew-snaatak) for 1 hour, providing a justification or ticket reference.
2. Authentication & Policy:
The Hoop Gateway authenticates the developer via the Identity Provider (IdP) and evaluates the request against the Policy Engine (FR3).The policy specifies that access to production VMs requires approval.
3. Review Workflow:
The access request is forwarded to an Approver through the configured integration (e.g., Slack, Jira, or Email).The Approver can approve or reject the request.
4. Session Start:
Once the request is approved, the Hoop Gateway establishes a secure, time-bound SSH session for the developer.The session is brokered through Hoop – without sharing the actual VM credentials or SSH keys with the user.
5. Data Flow (VM Access):
-
- The developer initiates the session using the Hoop CLI:dev-ashwathama-app-sonarqube-cloud-ops-crew-snaatak
- The connection is routed through the Hoop Gateway, which enforces session policies such as time limits and command restrictions (if configured).
- The developer executes commands directly on the VM (e.g., checking logs, validating service status, restarting services if permitted).
- All commands and outputs flow through the Hoop-controlled secure channel – no direct network access to the VM is exposed to the developer.
6 Audit:
The Audit Module (NFR – Auditability) records the entire lifecycle of the access, including:
-
- The access request details
- Approver decision
- Start and end timestamps
- Commands executed on the VM
- Full session logs (if session recording is enabled)
Deployment and Operational Considerations
1. Deployment Model
Hoop supports flexibility in deployment:
- Managed Service (SaaS): The fastest deployment option, where Hoop manages the core Gateway and services. Users only connect their target infrastructure and IdP.
- Self-Hosted: The entire platform can be deployed within the customer’s own infrastructure using standard tools: Docker, Kubernetes, or AWS deployment templates.
2. Operational Requirements
- Identity Management: Requires integration with an existing Identity Provider (IdP) for user authentication and group synchronization.
- Secrets: If using the Secrets Management feature, integration with a corporate Secrets Manager is required.
- Configuration: All policy configuration, runbook definitions, and connection details are managed through the Hoop control plane (web app or API).
User Access & Connection Guide (Azure AD + Hoop Access Flow)
This section provides a practical guide for administrators and end-users on how to authenticate into Hoop, assign access, and connect to VMs using both the Web Terminal and the CLI.
1. Login to Hoop (All Users)
- Open the Hoop identity portal: http://identity.opstree.dev
- Click Sign in with Azure AD.
- You will be automatically logged in if your Azure AD account is valid.
2. Admin Workflow: Grant Access to Users / Teams
- Navigate to Organisation → Users.
- Select a user and click Edit.
- Assign the required Group to the user.(Access policies are tied to Groups, not individual users.)
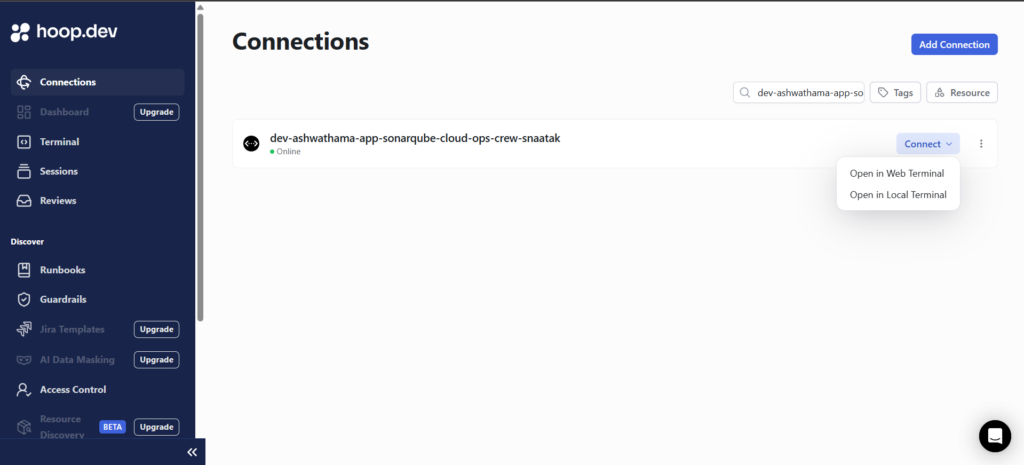
3. User Workflow: Connect to VMs via Web Terminal
- Open the Hoop Web Dashboard.
- Navigate to Connections.
- Select the target VM/server.
- Click Connect.
- A browser-based SSH terminal opens—no local SSH configuration required.
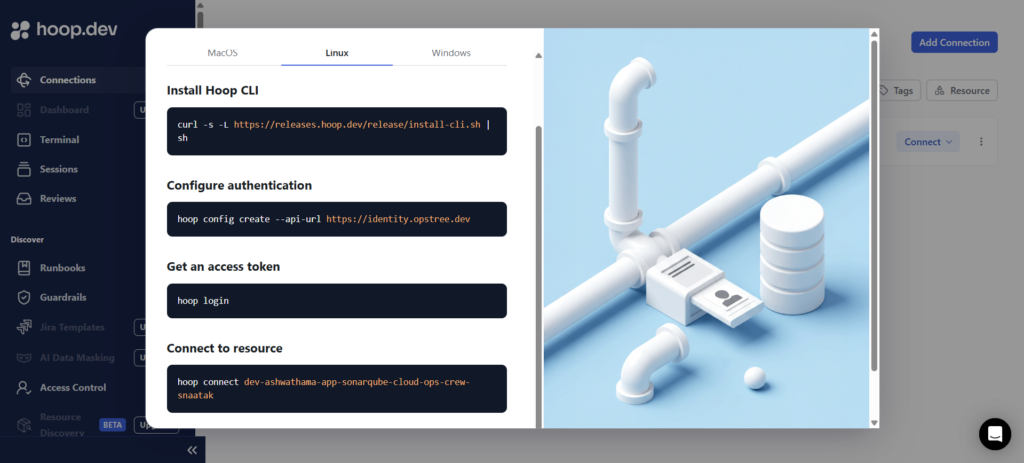
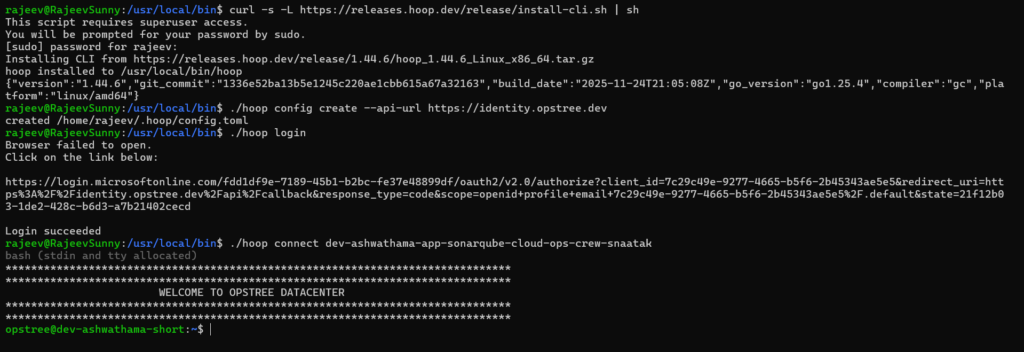
4. User Workflow: Connect to VMs via CLI
Install the Hoop CLI
hoop login
View available servers
hoop ls
Connect to a server
hoop connect <connection-name>
Cost Savings with Hoop
Implementing Hoop provides tangible cost reductions across security, DevOps operations, engineering productivity, and compliance. Below are the key areas where organizations achieve measurable savings:
1. Reduced Operational Overhead
- Eliminates manual user onboarding/offboarding for server access.
- No need to distribute, rotate, or manage SSH keys across environments.
- Centralized policy and access control reduces admin time.
Savings: Fewer DevOps hours spent on access management (typically 20–40% reduction).
2. Lower Security & Credential Risks
- Removes shared credentials and permanent access.
- Prevents accidental exposure of database credentials or SSH keys.
- Reduces time spent investigating access-related security incidents.
Savings: Avoids costly security breaches, investigations, and downtime.
3. Faster Developer Access
- Developers get timely, self-served access (via reviews) instead of waiting for Ops.
- No jump hosts, VPN approvals, or key setups required.
- Enables direct access via browser terminal or CLI.
Savings: Developer productivity increases (15–25% faster incident resolution).
4. Reduced Compliance Costs
- Full session recordings and audit logs simplify compliance checks.
- Automated data masking reduces risk of PII exposure audits.
- Helps meet SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA with lower audit overhead.
Savings: Lowers annual compliance effort by 30–50%.
5. Eliminates Multiple Legacy Tools
Hoop replaces several traditional access tools:
- Bastion hosts
- VPN solutions
- SSH key management systems
- Sudo policy systems
- Manual audit logging tools
Savings: Lower infrastructure + licensing + administrative cost.
Overall Impact:
Organizations typically see 25–50% reduction in access-management operational costs and faster developer throughput.
Competitor Comparison
Hoop operates in the privileged access and secure developer access ecosystem. Below is an overview of how Hoop compares with major alternatives.
1. Teleport
Strengths:
- Strong in Kubernetes access.
- Good for cloud-native engineering environments.
Limitations vs. Hoop:
- No AI-powered data masking.
- Heavier operational overhead for self-hosting.
- Review workflows are less flexible.
- Not as seamless for database query monitoring.
Hoop Advantage:
Simpler access workflow, lighter deployment, and better protocol-aware masking.
2. StrongDM
Strengths:
- Excellent database proxying.
- Good user/group permissioning.
Limitations vs. Hoop:
- Expensive for large teams.
- Lacks AI guardrails and runbooks.
- Limited automation around command filtering.
Hoop Advantage:
More cost-effective, includes guardrails + runbooks natively.
3. HashiCorp Boundary
Strengths:
- Open-source and enterprise-ready.
- Strong integration with HashiCorp tooling.
Limitations vs. Hoop:
- No data masking.
- No session recording out of the box.
- Complex to deploy and maintain.
Hoop Advantage:
Faster setup, built-in audits, and full masking + review workflows without add-ons.
4. Bastion Hosts / Jump Servers (Legacy)
Strengths:
- Simple to set up.
- Familiar for traditional Ops teams.
Limitations vs. Hoop:
- No approvals.
- No session recording.
- No policy/guardrails.
- Complete lack of auditability.
- Shared credentials remain a big risk.
Hoop Advantage:
Modern, secure, automated, and fully auditable.
5. VPN + SSH Key Setup (Traditional Access)
Limitations:
- Keys stored on developer laptops.
- Very slow onboarding and offboarding.
- Difficult to enforce least privilege.
- No masking, no analytics, no audit logs.
Hoop Advantage:
Eliminates keys, VPN dependency, and fragile network-level access.
Why Teams Choose Hoop
- Lightest operational footprint
- Fastest time-to-setup
- Strongest security-to-cost ratio
- Only tool with AI Guardrails + Protocol-level Data Masking + Runbooks
- Better suited for engineering teams handling sensitive data (PII, payments, logs)
Conclusion
Hoop provides a modern, centralized, and secure way to manage access to production infrastructure without relying on static credentials, shared SSH keys, or manual break-glass procedures. By enforcing policy-driven, time-bound access with integrated reviews, guardrails, and full session auditing, Hoop helps organizations significantly reduce operational risk while improving developer efficiency. Whether deployed as a managed SaaS or fully self-hosted, the platform fits seamlessly into existing identity, secrets, and approval ecosystems.
With its AI-powered data masking, intelligent command filtering, and Git-based runbooks, Hoop not only strengthens security but also accelerates day-to-day operations. For teams striving for compliance, auditability, and scalable access governance, Hoop Access Gateway offers a future-ready solution that balances control with productivity.
Related Searches – Data pipeline development services | DevOps Service Provider | AWS Consulting Partner
