This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of container scanning tools, exploring their importance in modern software development, the types of vulnerabilities they detect, and a comparison of popular tools available in the market. We will delve into the benefits of integrating container scanning into your CI/CD pipeline and offer guidance on selecting the right tool for your specific needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Container Scanning
- Why is Container Scanning Important?
- Types of Vulnerabilities Detected by Container Scanning Tools
- Popular Container Scanning Tools
- Integrating Container Scanning into Your CI/CD Pipeline
- Choosing the Right Container Scanning Tool
- Best Practices for Container Scanning
- Real-World Case Studies of Container Scanning
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction to Container Scanning
Containers have revolutionized software development and deployment, offering portability, scalability, and efficiency. However, they also introduce new security challenges. Container images often contain vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software components that can be exploited by attackers.
Container scanning tools are designed to identify these security risks, enabling developers and security teams to proactively address them before deployment.
Enterprise DevSecOps Services to automate secure CI/CD pipelines enforce continuous compliance and accelerate cloud native application delivery
Why is Container Scanning Important ?
- Early Vulnerability Detection: Container scanning identifies vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle, allowing developers to fix them before they reach production. This reduces the cost and effort associated with remediation.
- Improved Security Posture: By regularly scanning container images, organizations can maintain a strong security posture and reduce their attack surface.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries and regulations require organizations to implement security measures, including vulnerability scanning. Container scanning helps organizations meet these compliance requirements.
- Reduced Risk of Exploitation: By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, container scanning reduces the risk of successful attacks and data breaches.
- Faster Remediation: Container scanning tools provide detailed information about vulnerabilities, including their severity, location, and recommended remediation steps. This enables developers to quickly and effectively address security issues.
End to end cloud migration and modernization services with automated CSPM controls identity security and continuous compliance enforcement.
Types of Vulnerabilities Detected by Container Scanning Tools
Container scanning tools can detect a wide range of vulnerabilities, including:
- Operating System Package Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities in the operating system packages installed within the container image.
- Application Dependencies Vulnerabilities: These are vulnerabilities in the application dependencies, such as libraries and frameworks, included in the container image.
- Configuration Issues: These are misconfigurations in the container image or runtime environment that can expose the application to security risks. Examples include exposed ports, insecure default passwords, and overly permissive file permissions.
- Secrets and Credentials: Container images may inadvertently contain sensitive information, such as API keys, passwords, and certificates. Container scanning tools can detect these secrets and prevent them from being exposed.
- Malware: Container scanning tools can detect malicious software that may be present in the container image.
- Outdated Software: Scanning tools can identify outdated software components that are known to have vulnerabilities.
Popular Container Scanning Tools
Several container scanning tools are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here’s a comparison of some popular options:
- Trivy: Trivy is an open-source vulnerability scanner that is easy to use and integrates well with CI/CD pipelines. It supports scanning container images, file systems, and Git repositories. Trivy is known for its speed and comprehensive vulnerability database.
- Anchore Engine: Anchore Engine is an open-source container analysis and policy enforcement tool. It provides detailed information about container images, including their contents, vulnerabilities, and compliance status. Anchore Engine can be used to define policies that automatically block the deployment of vulnerable or non-compliant images.
- Aqua Security Trivy: Aqua Security offers a commercial version of Trivy with additional features, such as enterprise support, advanced reporting, and integration with other security tools.
- Snyk Container: Snyk Container is a commercial container scanning tool that focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in application dependencies. It provides detailed information about vulnerabilities, including their severity, impact, and recommended remediation steps. Snyk Container also offers features for automatically fixing vulnerabilities.
- JFrog Xray: JFrog Xray is a commercial universal artifact analysis tool that integrates with JFrog Artifactory. It provides vulnerability scanning, license compliance analysis, and impact analysis for container images and other software artifacts.
- Clair: Clair is an open-source vulnerability scanner that is designed to be integrated into container registries. It provides a REST API for scanning container images and retrieving vulnerability information.
- Amazon Inspector: Amazon Inspector is a vulnerability management service that automatically assesses the security of your Amazon EC2 instances and container images. It provides detailed findings about vulnerabilities and recommends remediation steps.
- Google Cloud Container Analysis: Google Cloud Container Analysis is a service that provides vulnerability scanning and metadata management for container images stored in Google Container Registry.
Integrating Container Scanning into Your CI/CD Pipeline
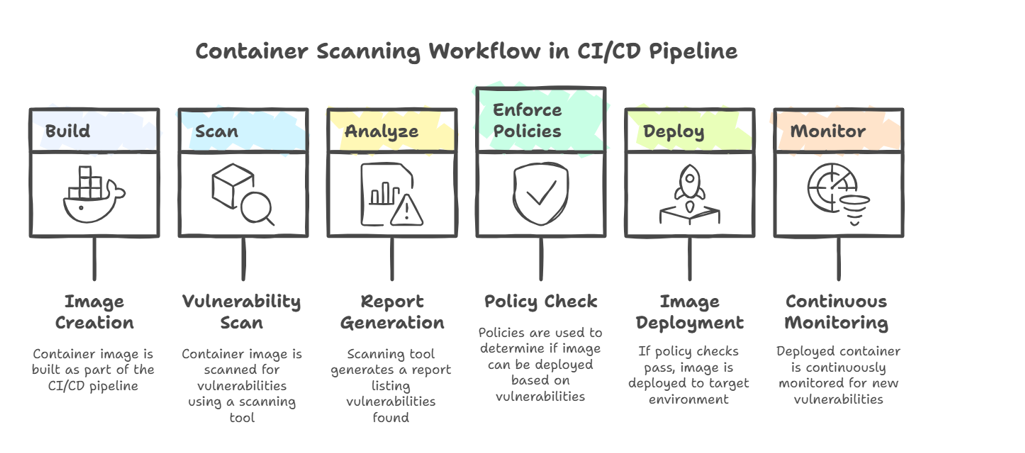
Integrating container scanning into your CI/CD pipeline is crucial for ensuring that vulnerabilities are detected and addressed early in the development lifecycle. Here’s a typical workflow:
- Build: The container image is built as part of the CI/CD pipeline.
- Scan: The container image is scanned for vulnerabilities using a container scanning tool.
- Analyze: The scanning tool generates a report that lists the vulnerabilities found in the image.
- Enforce Policies: Policies are used to determine whether the image is allowed to be deployed based on the severity and number of vulnerabilities.
- Deploy: If the image passes the policy checks, it is deployed to the target environment.
- Monitor: The deployed container is continuously monitored for new vulnerabilities.
Also Read: Top DevSecOps Tools in 2026
Choosing the Right Container Scanning Tool
Selecting the right container scanning tool depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider the following factors:
Best Practices for Container Scanning
- Scan Regularly: Scan container images regularly, ideally as part of your CI/CD pipeline.
- Automate Scanning: Automate the scanning process to ensure that all container images are scanned consistently.
- Prioritize Vulnerabilities: Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and impact.
- Remediate Vulnerabilities Promptly: Address vulnerabilities as quickly as possible to reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Keep Vulnerability Databases Up-to-Date: Ensure that your container scanning tool is using the latest vulnerability databases.
- Enforce Policies: Define and enforce policies that prevent the deployment of vulnerable container images.
- Monitor Deployed Containers: Continuously monitor deployed containers for new vulnerabilities.
- Train Developers: Train developers on container security best practices and how to use container scanning tools.
Real-World Case Studies of Container Scanning
To understand the practical impact of container scanning, here are four real-world examples from different industries showing how organizations improved security, compliance, and DevSecOps efficiency by adopting container scanning tools.
Case Study 1: FinTech Organization Using Snyk Container
A financial technology company handling sensitive payment data integrated Snyk into their CI/CD pipeline. Their initial scans revealed:
- Hardcoded API keys inside Docker images
- Outdated dependencies such as vulnerable OpenSSL and Log4j components
- Multiple high-severity CVEs in base images used across multiple applications
By enforcing automated scanning and fixing suggestions:
| Before Scanning | After Implementation |
|---|---|
| 400+ untracked vulnerabilities | 92% reduction in critical and high-risk CVEs |
| Manual reviews and no enforcement | Automated security gates in CI/CD |
| Weeks to detect and fix issues | Fixes applied within the same sprint |
Outcome: The organization successfully achieved PCI-DSS compliance and reduced security risks without slowing development velocity.
Case Study 2: Spotify Using Trivy for Cloud-Native Security
Spotify publicly shared their adoption of Trivy due to its speed, open-source flexibility, and seamless automation.
Challenges identified:
- Large microservices ecosystem with thousands of container images
- Difficulty prioritizing vulnerabilities across development teams
- Lack of unified scanning across environments
After implementing automated registry and CI scans:
- Vulnerability discovery time dropped from weeks to hours
- Teams adopted a shared remediation workflow
- A centralized policy framework was introduced to block high-risk images
Outcome: Spotify improved governance across containerized environments without adding operational overhead.
Case Study 3: Global E-Commerce Platform Using JFrog Xray
A major e-commerce company integrating JFrog Xray + Artifactory identified multiple high-risk vulnerabilities, including:
- Critical CVEs in OpenSSL (CVE-2022-0778)
- License compliance violations in open-source dependencies
Using automated scanning tied to image promotion workflows:
| Before | After |
|---|---|
| Vulnerabilities discovered post-deployment | Issues detected before reaching production |
| No visibility into dependency risks | Full dependency graph security insights |
| Manual review during releases | Automated scanning and policy-based approvals |
Outcome: The organization prevented vulnerable images from entering production and improved compliance management for open-source components.
Case Study 4: Healthcare Provider Using Anchore Enterprise
A healthcare organization operating under HIPAA regulations integrated Anchore to secure container workloads powering electronic health records.
Findings included:
- Excessive container permissions (root user defaults)
- Images containing unused and outdated software packages
- Possible PHI exposure risk through misconfigured environment variables
Security improvements included:
- Switching to minimal base images (Distroless/Alpine)
- Implementing strict Kubernetes admission controls
- Enforcing mandatory vulnerability remediation windows
Outcome: The company achieved HIPAA audit readiness and significantly reduced potential attack vectors.
Conclusion
Container scanning is an essential part of securing your containerized applications. By integrating container scanning into your CI/CD pipeline and following best practices, you can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities, reduce your attack surface, and improve your overall security posture. Choosing the right container scanning tool for your needs is crucial, so carefully evaluate the available options and select the tool that best meets your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is container scanning?
Container scanning is the process of analyzing container images to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, secrets, malware, and outdated software before they are deployed into production environments.
Why do we need container scanning if images come from trusted registries?
Even trusted or official images may have known vulnerabilities or outdated dependencies over time. New CVEs are discovered daily, so scanning ensures that your images remain secure throughout their lifecycle.
When should container scanning be performed?
Container scanning should be performed during:
- Development (local scans)
- CI/CD pipelines (automated blocking if severe vulnerabilities exist)
- Before deployment
- After deployment (continuous monitoring)
Which tools are most commonly used for container scanning?
Popular tools include:
- Trivy
- Snyk Container
- Anchore
- JFrog Xray
- Clair
- Amazon Inspector
- Google Cloud Container Analysis
Does container scanning slow down the CI/CD pipeline?
Some scans may take time, but most modern tools are optimized for speed. Incremental scanning, caching, and policy-based execution ensure minimal CI/CD delay.
