As I mentioned in my previous blog on Redis Best Practices that in my upcoming blog I will discuss about load testing on Redis so here I am ready with my blog in which I will explain how can we measure our Redis Performance. Although there are plenty of articles out there on this similar topic, but I want to share my experience as a DevOps. Also, I want to share the methods which we are implementing at our organization.
So, Load testing What, Why?
The first thought which comes to our mind is why do we need load testing, as our environment is already working fine. Or it is working fine since the first launch.
But Hey!!! let me tell you something it’s not simple as that, as we know everything has its own limits and knowing your limits is always helpful. When we are not ready to face the problem of the increasing load, our environment can easily collapse. There is saying as well
Prevention is better than cure
In simple words, it means it’s easier to stop something bad happening in the first place than to repair the damage after it happened.
So when I decided to test the redis performance, it was not quite easy to start, there are plenty of load testing frameworks were present but which to choose? So I did the comparison between various load testing framework. Although there is already Jmeter was available which is a popular load testing tool but I found it a bit complex to learn easily and rapidly and also it requires a hell lot of resources so I have chosen an awesome Python load testing framework, Locust, which is very lightweight and easy to setup load testing framework.
The golden rule before starting the load testing is that you should have metrics or a number in your mind which you want to achieve.
So I will be using my own organization load testing utility which we have created for Redis Load or Performance Testing.
You can find the code at- https://github.com/opstree/redis-load-test
So you can simply clone the git repo like this:-
git clone https://github.com/opstree/redis-load-test.git
As Locust is a python based project so it doesn’t have long dependencies list but surely it does have some dependency. So after repo cloning, we have to install these dependencies
cd Scripts
pip3 install -r requirments.txt
Once the dependency hurdle is crossed we can move to the step in which we will connect our utility to Redis. To achieve this we have a file called redis.json in the Scripts folder of the repo, you just have to update the redis details in that file. For example:-
{
"redis_host": "10.1.1.100",
"redis_port": "6379",
"redis_password": ""
}
Once you are done with connection details, kaboom you are all set to use the performance testing utility. Just go on the terminal and run this command.
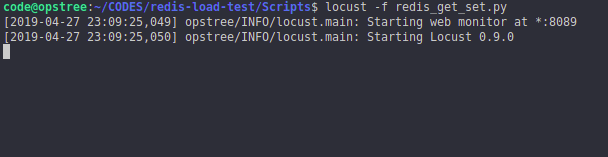
locust -f redis_get_set.py
The output will be something like this
Now go and open up the URL on the browser by http://your_ip:8089
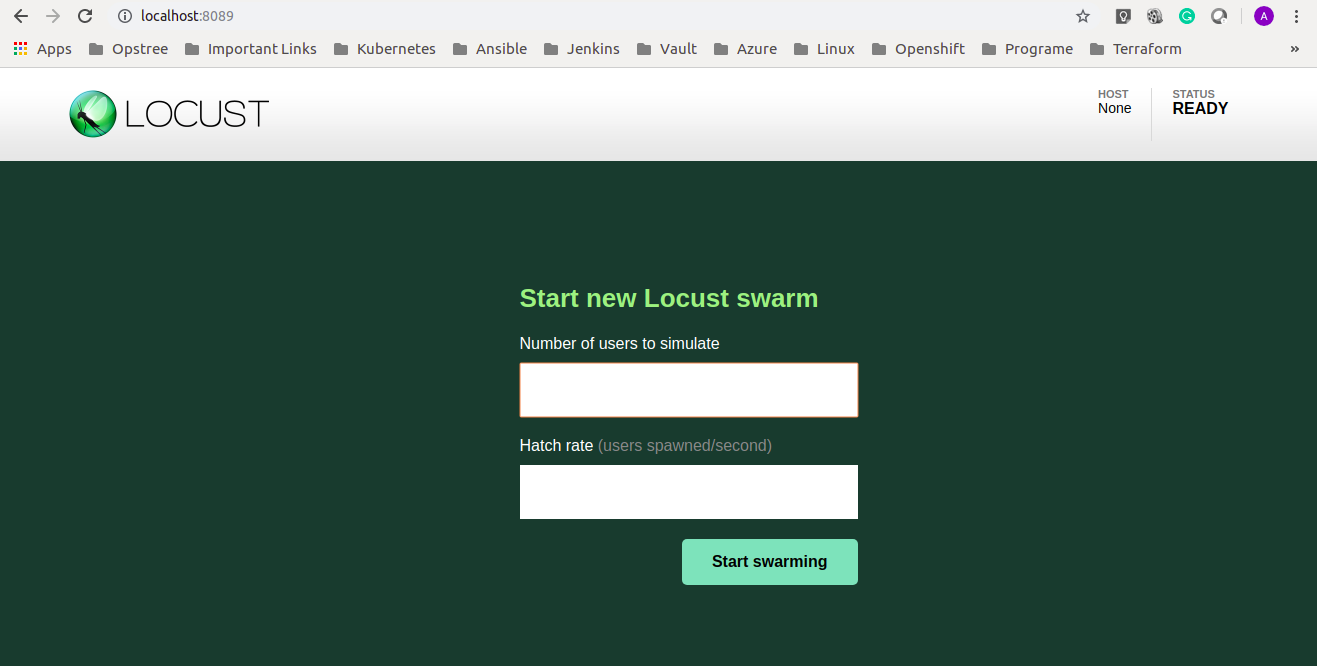
The UI page will look like this
You will have two empty blocks there:-
Number of users to simulate:- Total number of user connection request which you want to make.
Hatch Rate:- How quickly you want to spawn users.
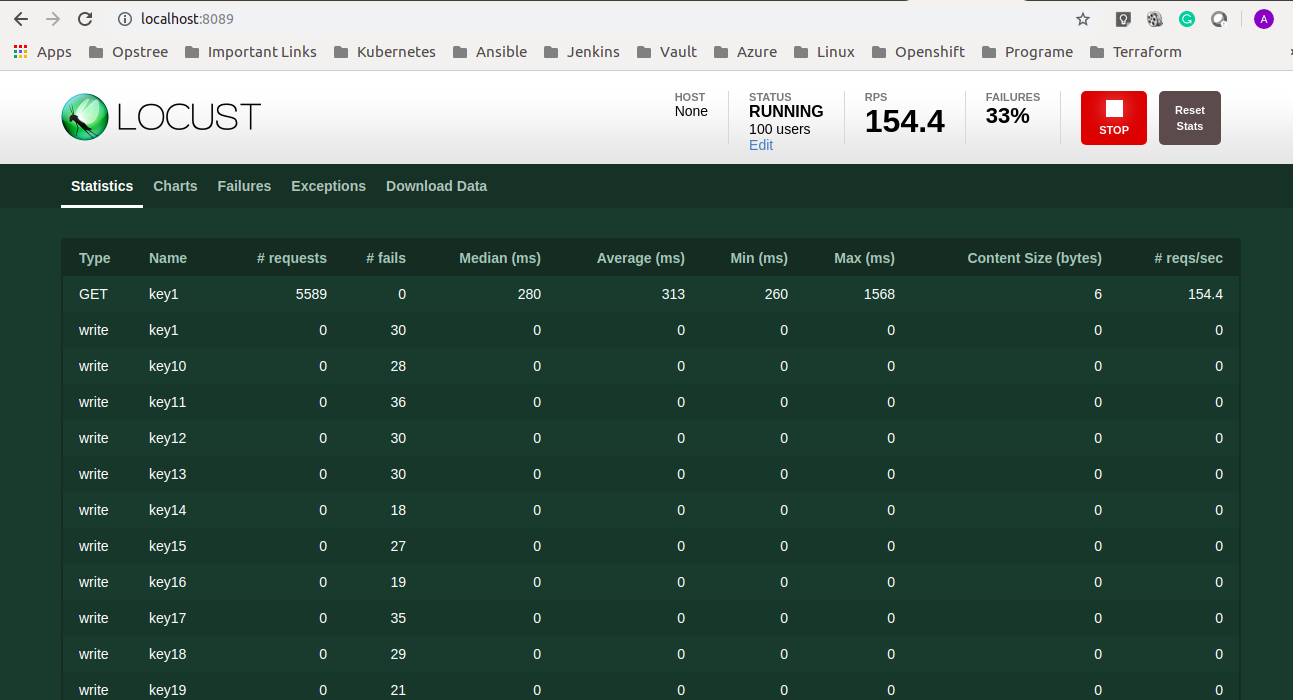
After filling these details you can simply start swarming and you can wait until it completes its execution. Once the execution will be completed you will have this kind of details.
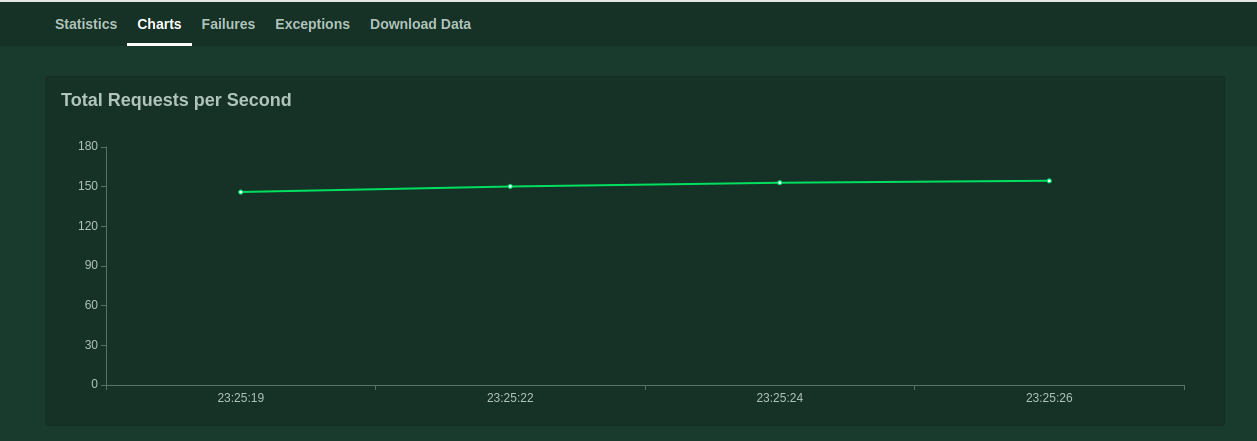
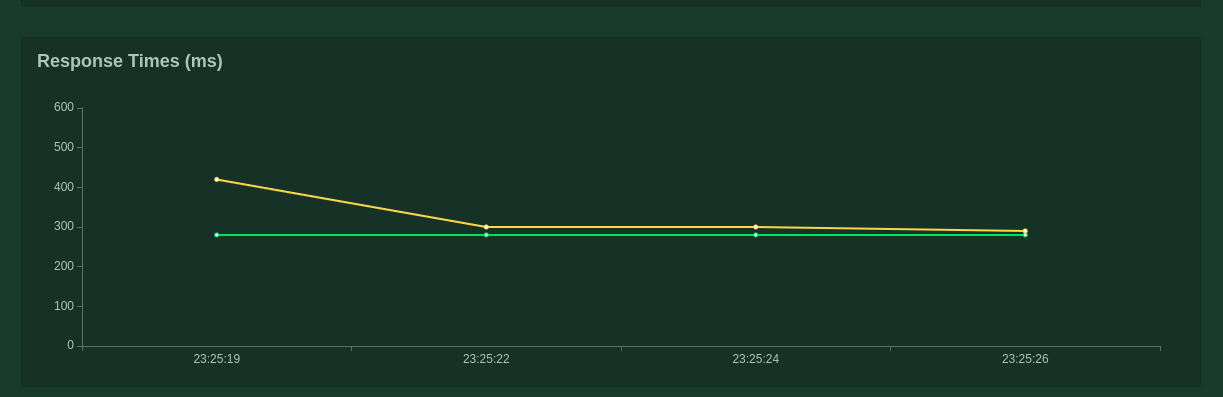
This page is loading data in the form of statistics but you can also see the data in a beautiful graph format on the same UI. For example-
I have also provided detailed information in the README file as well of the repo.
One of the benefits which I feel important in doing load testing is that you can set up a performance baseline according to your environment. And yes, if you are not getting the desired output of your Redis Performance you can check out our blog on Redis Best Practices and Performance Tuning.
The main idea of writing this blog was to encourage people to know the limitations of their environment and to make it ready for any kind of challenge.
I hope I explained everything clearly enough to understand. If you do have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to ask.
Cheers Till Next Time!!!