Introduction
As businesses continue to generate large amounts of data every day, it has become essential to establish a reliable cloud data storage architecture. Whether you’re working with analytics workloads, IoT data, or datasets for AI training, a thoughtfully designed cloud storage setup guarantees scalability, availability, and high performance while keeping costs and security under control.
In this guide, we will discuss designing a cloud data storage architecture suitable for big data, its components, best practices, and cutting-edge technologies that are fueling data-driven innovation.
What is cloud storage
Cloud storage refers to a model of cloud computing that allows you to store your data and files online through a cloud service provider. You can access this data via the public internet or a dedicated private network. The provider takes care of securely storing, managing, and maintaining the servers, infrastructure, and network, ensuring you can access your data whenever you need it, with virtually unlimited scale and flexible capacity. By using cloud storage, you eliminate the need to invest in and manage your own data storage infrastructure, giving you greater agility, scalability and durability, along with the convenience of accessing your data anytime and anywhere.
How Does Cloud Storage Work?
Cloud storage systems operate on a distributed architecture, where data is divided into smaller pieces and stored on multiple servers located in different physical regions. This arrangement ensures that if one server goes down, the data will remain accessible through copies stored on other servers, thereby achieving the required level of redundancy. When you upload a file, it travels via the internet to your cloud provider’s infrastructure. For security, the file is encrypted, fragmented, and replicated. Information about where a file is stored and who can access it is kept in a centralized index, making it easy to retrieve later.
Cloud storage is easily accessible through APIs or web interfaces. Users can read, write, and manage their data using tools such as SDKs or command-line utilities. Most providers also include features such as version control, access logs, and security measures, including encryption and permissions based on user identity.
Furthermore, cloud storage has the ability to automatically adjust to your needs. It can increase storage space and processing resources when needed and reduce them when they are no longer needed. This flexibility helps users keep costs under control while ensuring optimal performance.
Looking for a Cloud Database Management Service to securely store, manage, and scale your data with ease?
Types of Cloud Storage
1. Object Storage
This type is perfect for handling unstructured data, such as images, videos, audio files, and documents. It uses a flat structure where each piece of data is treated as an object, complete with a unique identifier. Object storage systems are highly scalable, enabling them to efficiently manage vast amounts of data. These are particularly effective for content distribution, backup, and archival tasks.
Popular Object Storage Services:
- Amazon S3
- Google Cloud Storage
- Azure Blob Storage
2. File Storage
Cloud file storage mimics traditional file systems and organizes data into directories and subdirectories. This structure is suitable for structured data that requires hierarchical organization. File storage is commonly used for document sharing and collaboration, user file management, and hosting web content.
Leading File Storage Services:
- Amazon EFS
- Google Cloud Filestore
- Azure Files
3. Block Storage
Block storage provides raw storage volumes that can be directly attached to virtual machines (VMs) for various applications, such as databases and enterprise software. Unlike object and file storage, block storage doesn’t categorize data into files or objects. Instead, it represents storage as a sequence of blocks that can be written to and read from. This low-level access provides significant flexibility, but it also requires careful management by the user.
Top Block Storage Services:
- Amazon EBS
- Google Persistent Disk
- Azure Disk Storage
[ Also Read: Empowering Data Engineering Teams with Serverless Architecture]
Why Cloud Data Storage for Big Data?
In our current data-driven landscape, optimizing cloud storage solutions for big data is essential. This not only increases efficiency but also enhances scalability and keeps costs under control.
As organizations collect and manage large amounts of data, neglecting proper storage management can cause significant performance issues and disrupt budget plans.
1. Scalability
Big data environments can produce terabytes or even petabytes of information daily. An efficient storage architecture is crucial to ensuring that your system can scale seamlessly and easily accommodate growing data volumes without compromising performance or availability.
2. Performance
Quick and reliable access to data is crucial for real-time analytics and informed decision-making. By refining data storage practices, companies can minimize latency, speed up query responses, and gain quicker insights from their analytics and AI initiatives.
3. Cost Management
Managing the storage of large datasets can be quite expensive. Optimizing your data storage approach can reduce unnecessary costs using strategies like data tiering, Compression and lifecycle management ensure that only the most valuable data consumes high-cost resources.
[ Case Study: Empowering a High-Growth E-Commerce Platform with a Modern Data Stack]
What Is Big Data?
Big data presents unique challenges in data management that traditional databases struggle to address due to the ever-increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data.
Most often reference is made to the famous “three Vs”:
- Volume: This involves massive amounts of data, typically ranging from terabytes to petabytes.
- Variety: Data comes from a variety of sources and formats, including web logs, social media interactions, e-commerce and online transactions, financial transactions, etc.
- Velocity: Businesses are now under pressure to process data in a timely manner. From data preparation to providing actionable insights to users, Deadlines can often be tight, requiring collection, storage, processing, and analysis at intervals ranging from daily to real-time.
[ Good Read: The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Data Engineering with Azure, ADF, and Databricks]
AWS Solutions for Big Data
AWS offers a comprehensive platform packed with customized solutions for developers, analysts, and marketers. AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a branch of Amazon that offers a vast range of on-demand cloud computing services and products. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS caters to a variety of needs, including developer tools, email, Internet of Things (IoT), mobile development, networking, remote computing, security, servers and storage, etc. This platform primarily consists of two major products: EC2 (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud), which serves as Amazon’s virtual machine service, and S3, which is a scalable solution for data object storage.
Cloud Data Storage Architecture
The cloud data platform architecture is built on four major layers: data ingest, data storage, data processing, and data serving. Each layer represents a critical component that provides unique functionalities to the overall platform.
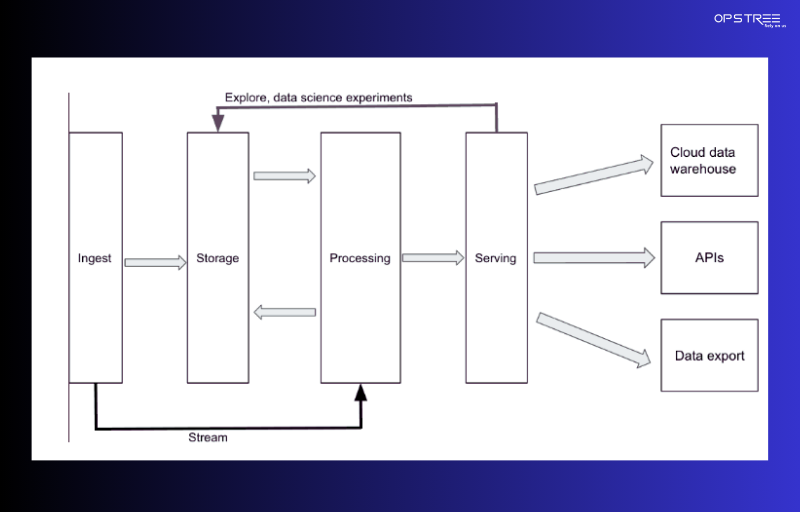
Data Ingest Layer
In the data ingest layer, components connect various source systems to the cloud platform, easing the transfer of data to cloud storage. These ingestion tools should be versatile, able to accommodate various data sources, and support both batch and real-time data ingestion.
Although some data normalization and transformation may occur during this step, best practices suggest keeping the data in its original format. This approach allows for more flexible analysis without the need for re-ingestion from the source.
Data Storage Layer
After passing through the ingestion layer, the raw data is stored in the data storage layer. Public cloud providers offer efficient object storage solutions, allowing enterprises to store and retain large amounts of data in a cost-effective manner.
Cloud storage is not only economical but also has scalability and high reliability. Cloud vendors like AWS offer exceptional failover and recovery options, allowing organizations to adjust their storage capacity as needed.
Data Analytics/Processing Layer
In the data processing layer, various components play a vital role in extracting information from storage systems. They use normalization techniques, perform transformations, and apply business logic to convert raw data into structured and meaningful insights that can be leveraged in the future.
Data Serving Layer
The data services layer is the last major component of the cloud data platform architecture. Here, software components serve to deliver the results obtained from the data analysis and processing layer to the consumers who need that information. This layer typically features a cloud data warehouse for storing relational tables, but can also include different deployments such as a data lake, data lakehouse, or data mart.
Available AWS Tools for Big Data
To effectively tackle the challenges of big data, it’s essential to have the right tools. Transforming vast amounts of raw data into actionable insights may seem daunting, but with the right resources, it’s certainly possible.
Luckily, AWS provides an extensive array of tools and solutions tailored to address the unique challenges associated with different big data sectors. Let’s explore some of these invaluable resources.
As a leading AWS service provider, it enables organizations to design, manage, and scale robust data storage and analytics architectures with ease.
Data Ingestion
Amazon Kinesis Firehose is a fully managed service designed to make it easy to acquire and deliver real-time streaming data on AWS. It takes care of essential tasks like data compression, batching, and encryption, and even allows AWS Lambda functions to transform the data before storing it.
The service reliably streams data to Amazon S3, data lakes, data stores, and analytics platforms, ensuring everything integrates smoothly into a cloud data storage setup. It automatically adjusts to changes in data volume, eliminating the need for manual management, and making it suitable for organizations dealing with large-scale, dynamic data environments.
AWS Snowball
AWS Snowball is a robust solution designed to help you efficiently and securely move large amounts of data from your on-site storage systems and Hadoop clusters directly to your S3 buckets. When you initiate a job through the AWS Management Console, a Snowball device is immediately dispatched to your location. Simply connect it to your local area network, install the Snowball client, and transfer your files and folders to the device. After completing the transfer, you just need to send Snowball back to Amazon Web Services, and they will take care of transferring your data to your S3 bucket.
Data Storage
Speaking of S3, Amazon S3 stands out as a highly scalable, secure, and durable object storage service that can accommodate any type of data from various sources. Whether it’s data from corporate applications, websites, mobile devices, or IoT sensors, S3 provides an unmatched level of availability for any data you store. Its infrastructure is similar to what Amazon uses for its global e-commerce operations, which is a strong testament to its reliability.
AWS Glue
AWS Glue serves as an essential data service that centralizes metadata into repositories, thereby streamlining the ETL (extract, transform, load) process. Data analysts can easily create and execute ETL jobs with just a few clicks from the AWS Management Console. The built-in data catalog serves as a persistent metadata store for all your data assets, enabling analysts to easily find and query everything from a consolidated view.
Data Processing
Since Apache Spark and Hadoop are widely used data processing frameworks, it is beneficial to have an AWS tool that integrates well with them. This is where Amazon EMR comes in, providing a managed service that efficiently processes vast amounts of data. EMR supports 19 different open-source projects, including Spark and Hadoop. It also features managed EMR notebooks, which are perfect for collaboration, data engineering, and data science development.
Redshift
Amazon Redshift empowers analysts to execute complex analytical queries on vast amounts of structured data at incredibly low cost – approximately 90% lower than traditional processing options. An outstanding feature of Redshift is Redshift Spectrum, which allows data analysts to execute SQL queries directly on exabytes of structured and unstructured data in S3, eliminating unnecessary data transfers.
Visualization
Amazon QuickSight is an AWS service designed to create stunning visualizations and interactive dashboards, easily accessible from any mobile device or web browser. This business intelligence tool combines AWS’s lightning-fast parallel processing with its super-fast, parallel, in-memory calculation engine (SPICE), helping you quickly perform data calculations and create impressive graphs.
What are cloud storage use cases?
Cloud storage plays a vital role in application management, data management, and ensuring business continuity. Here are some examples:
1. Analytics and Data Lakes
Traditional on-premises storage often suffers from cost, performance, and scalability issues over time. In contrast, analytics requires large, affordable, and easily accessible storage options called data lakes.
Data lakes that leverage object storage retain data in its native format and come with extensive metadata, facilitating selective extraction for deeper analysis. These cloud-based solutions can serve as a central hub for various data warehousing, processing, big data, and analytical tools, allowing you to complete projects more quickly and effectively.
2. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data protection and access depend on reliable backup and disaster recovery solutions, yet it can be difficult to keep pace with growing storage demands. Cloud storage offers low cost, high durability, and impressive scalability for these needs. With built-in data management policies, you can automatically move data to more cost-effective storage based on usage patterns and timeframes.
Additionally, archival options can help businesses meet legal or regulatory mandates. This is particularly beneficial in sectors such as financial services, healthcare and life sciences, and media and entertainment, where large amounts of unstructured data require long-term retention.
3. Software Testing and Development
Developing and testing software typically involves setting up separate, independent storage systems, which requires substantial time and upfront capital investment. Leading companies are now streamlining this process by leveraging the flexibility, performance, and affordability of cloud storage. Even basic static websites can be upgraded without significant cost. IT professionals and developers are increasingly adopting pay-as-you-go storage solutions, reducing the burden of management and scaling.
4. Cloud Data Migration
The cost-effectiveness, durability, and availability of cloud storage can be attractive. However, IT staff who manage storage, backup, networking, security, and compliance may have legitimate concerns about moving large data sets to the cloud.
For some, embracing this change can feel overwhelming. Fortunately, hybrid, edge, and data movement services help you transition from the physical world to the cloud by simplifying the process of data migration.
5. Compliance
Storing sensitive data in the cloud raises important questions about regulation and compliance, especially if the data is already managed by compliant storage systems. Cloud compliance controls aim to allow you to effectively implement and manage end-to-end compliance measures across your data, ensuring you meet the requirements of regulatory bodies around the world. Through a shared responsibility model, cloud providers enable their customers to manage risk efficiently within their IT environments while demonstrating effective risk management through adherence to established and widely recognized frameworks.
6. Cloud-native Application Storage
Cloud-native applications leverage technologies such as containerization and serverless computing to quickly respond to customer needs in dynamic environments. These applications consist of small, independent components known as microservices that communicate by sharing data or state Cloud storage services support data management for these applications, and provide solutions to the current challenges of storing data in the cloud.
7. Hybrid Cloud Storage
Many businesses aim to take advantage of the benefits of cloud storage, yet they still operate on-premises applications that require quick access to their data or require rapid data transfer to the cloud. Hybrid cloud storage architectures connect on-premises systems with cloud storage, helping to reduce costs, lighten management workloads, and foster innovation with your data.
8. Database Storage
Block storage is preferred by many organizations for transactional databases due to its high performance and ability to be easily updated. With minimal metadata, block storage provides extremely low latency, which high-performance workloads and latency-sensitive applications, such as databases, require.
Using block storage, developers can create a flexible, scalable, and efficient transaction database. Since each block operates independently, the database continues to perform optimally even as the amount of stored data increases.
9. ML and IoT
Cloud storage enables the processing, storage, and analysis of data close to your applications, while also allowing data to be copied to the cloud for deeper analysis. With cloud storage, you can achieve efficient and cost-effective data storage while supporting machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics, driving insights and innovation for your business.
Conclusion
Building a reliable cloud data storage framework for big data is crucial for organizations striving for scalability, performance, and security in our increasingly data-centric world.By utilizing cloud-native tools and services like Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, or Google Cloud Storage, companies can effectively manage large datasets, guarantee smooth data access, and enhance their capabilities for advanced analytics. Thoughtfully designed architecture not only cuts costs and increases flexibility, but also sets the stage for AI, machine learning, and real-time decision-making. Ultimately, investing in a robust cloud data storage approach helps businesses transform raw data into valuable insights, foster innovation, and ensure long-term success.
