If you’re using AWS, you may have noticed data transfer fees being added to your expenses. These costs are often included in your cost and usage reports, but don’t be fooled, if they’re not monitored they can quickly add up and become a significant contributor to your AWS bills.
Many organizations may face unexpectedly high data transfer charges, which reach up to lakhs of rupees per year. To get a handle on these costs and potentially reduce them, it’s essential to get a clear picture of your data transfer costs and identify which resources are driving them.
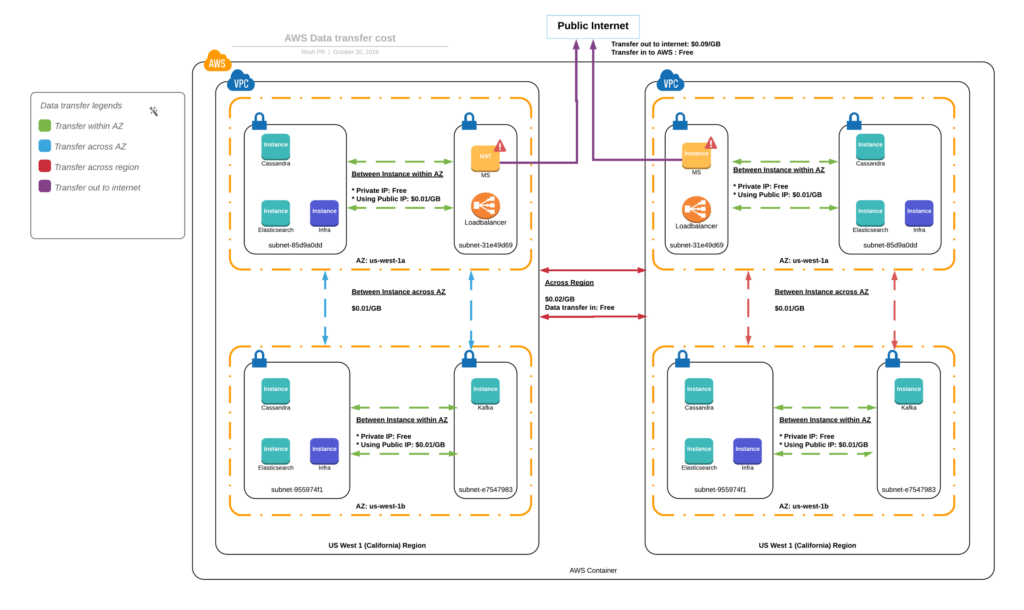
What Are AWS Data Transfer Costs?
AWS has a pricing structure for data transfers, applicable both to the exchanges between its services-like Amazon EC2 and S3 , and between those services and the internet.
It’s worth noting that some AWS services bundle data transfer costs into their pricing, rather than billing separately. For instance, when using Kinesis on AWS, you might not see a clear data transfer fee.
However, in other cases, you could incur charges for transferring data in one direction but not the other-such as moving data across AWS S3 regions. Additionally, there are different fees for data transfers in and out, particularly when dealing with EC2 instances located in different availability zones.
Clearly, there are numerous factors at play. To manage data costs effectively, it’s crucial to have a good grasp of how your data is shared and the associated charges.
Here’s how it breaks down:
· Data Transfer In (Ingress): This is when you upload data to AWS services, like putting files in an S3 bucket or sending information to an EC2 instance. Good news: This is typically free.
· Data Transfer Out (Egress): When you’re downloading data or serving it to end-users, like serving images from your S3 bucket to your app’s users, AWS charges you. These costs can get pricey if you’re dealing with a lot of data.
· Inter-Region Data Transfer: When transferring data from one AWS region to another, such as moving files from S3 in Virginia (us-east-1) to Oregon (us-west-2), be aware that AWS applies charges for this service.
· Intra-Region Data Transfer: Even if your data remains within the same AWS region, transferring it between different availability zones or services may still lead to additional fees.
Key Factors That Influence Data Transfer Costs
As you learn about AWS data transfer costs, you’ll quickly discover that it’s not a straightforward topic. There are several factors that can affect your final bill:
· Source and Destination: The cost of transferring data depends on the starting point and the ending point. For example, transferring data between regions incurs higher charges than transferring data within the same region. Additionally, sending data over the Internet typically costs more than internal AWS transfers.
· Volume of Data: Similar to how mobile providers charge based on your data usage, AWS applies charges based on the amount of data you transfer. More gigabytes (GB) equal greater expenses.
· AWS Services Involved: Pricing varies across different AWS services. For example, transferring data out of S3 comes with a different cost structure than moving data out of EC2.
· Geography Matters: Certain regions carry higher data transfer costs due to varying infrastructure and operational expenses. Therefore, it’s smart to consider the region carefully when planning your architecture.
Common Scenarios Where Data Transfer Costs Apply
Let’s take a look at a few situations where AWS data transfer fees will likely impact your bill:
1. Content Delivery:
If you’re using Amazon CloudFront to serve static content (like images, videos, or other media), you’re going to pay for data transfer based on the volume of content served to your users. So, if your website or app starts getting lots of traffic, those content delivery fees can rise quickly.
2. Backup and Disaster Recovery:
Large-scale backups or data replication to multiple regions are crucial for business continuity. However, these processes can incur significant data transfer costs as data moves between AWS services and across regions.
3. Hybrid Cloud Architectures:
Many businesses run a mix of on-premises and cloud services. Transferring data between your on-prem environment and AWS can lead to egress charges, especially if you’re not careful about optimizing those data flows.
4. Multi-Region Deployments:
If your app operates in multiple AWS regions to reduce latency or serve global users, be prepared for inter-region data transfer costs. Those inter-region data charges can pile up quickly if your app is pulling or pushing data across continents.
[ Good Read: Achieving 30% AWS Cost Reduction in Just 8 Weeks ]
How to Keep AWS Data Transfer Costs in Check
The good news is, you don’t have to sit back and let data transfer fees eat away at your profits. There are several strategies you can adopt to minimize these costs:
1. Optimize Data Transfer Patterns:
Reduce unnecessary data transfers by caching content at edge locations (like Amazon CloudFront) to serve users faster without always fetching data from the origin.
2. Use AWS Direct Connect:
If you’re transferring a lot of data between your on-premises systems and AWS, consider using AWS Direct Connect. It’s a dedicated network connection that can save on costs compared to internet-based transfers.
3. Leverage the Free Tier:
AWS offers a Free Tier with limited data transfer allowances, which can be a godsend if you’re just starting. Make sure to leverage free transfers within the same region (e.g., for S3), and keep an eye on the free limits.
4. Compress Your Data:
Before transferring large files, try compressing them. Smaller files mean lower data transfer costs.
5. Pick the Right AWS Region:
Choosing a region closer to your users can minimize egress costs. For example, if most of your users are in Europe, hosting in the EU region could cut down on data transfer charges compared to hosting in the US.
6. Monitor Your Usage:
Use tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets to monitor your data transfer usage. By actively monitoring your costs, you can identify patterns that need optimization.
A Real-World Example: Breaking Down the Costs
Let’s bring this to life with a simple example. Imagine you run a web application hosted on AWS and serve 100 GB of data to users every month. Here’s how the data transfer costs might stack up:
· Data Transfer Out to Internet (First 10 GB): Free (thanks to AWS Free Tier).
· Data Transfer Out to Internet (Next 40 GB): $0.09/GB x 40GB = $3.60
· Data Transfer Out to Internet (Remaining 50 GB): $0.085/GB x 50GB = $4.25
Total Monthly Data Transfer Cost: $7.85
It seems pretty reasonable, right? But as your app grows, those costs could quickly balloon. With high traffic or large-scale data operations, these charges could escalate.
Conclusion: Be Smart About Your Cloud Spending
AWS data transfer costs can sneak up on you if you’re not paying attention. But with a bit of planning, strategy, and the right tools, you can manage and even reduce those costs effectively.
The key is to understand how data transfer works, monitor your usage, and design your architecture with cost efficiency in mind. Whether you’re using the Free Tier, optimizing your data transfer patterns, or choosing the right AWS region, smart planning can ensure that you’re not just scaling your app-but doing so affordably.
By keeping an eye on your data flow and implementing some cost-saving practices, you’ll be able to make the most of your AWS setup-without worrying about surprise bills at the end of the month.
FAQs
1. What are AWS data transfer costs and why do they matter?
AWS data transfer costs refer to the charges incurred when transferring data between different AWS services, between regions, or over the public Internet.If these costs are not carefully tracked and managed, they can quickly add up and have a huge impact on overall cloud spend.
2. What are some common scenarios that lead to high AWS data transfer charges?
High costs often arise from moving data between regions, sending data over the public Internet, or generating cross-AZ traffic between services like EC2 instances or load balancers that are not cost-optimized.
3. Why is understanding AWS data transfer costs important for cloud cost optimization?
Having a solid understanding of these costs helps teams develop cost-efficient architectures, prevent unexpected bills, and align cloud usage with their business goals. This knowledge is critical to achieving long-term savings and managing cloud finances effectively.

