Introduction
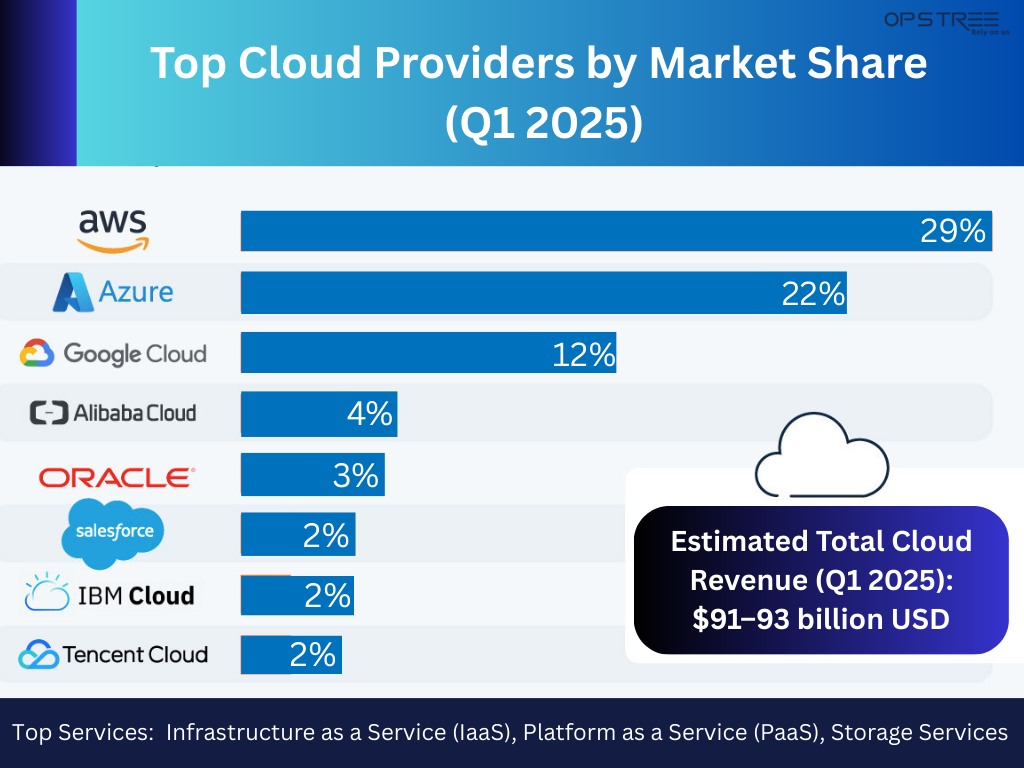
Amazon’s cloud computing division, Amazon Web Services (AWS), will remain a powerful entity in the global cloud infrastructure market by 2025, holding a remarkable 30% market share.
Comprehensive Services
With over 200 full-featured services from compute and storage to databases and machine learning.
Global Reach
Serving customers in over 190 countries across startups, enterprises, and government agencies.
Major companies such as Airtel, Netflix, Twitch, Paytm, LinkedIn, and Adobe are notable users of AWS Services.
Success Story
Discover how OpsTree enabled a 27% AWS cost reduction for a leading Indian fintech platform by optimizing their database infrastructure. Serving over 50 million users with digital wallets, bill payments, and mobile recharges, the client needed scalable yet cost-effective solutions. Our strategic intervention streamlined resource usage without compromising performance. Our strategic intervention streamlined resource usage without compromising performance.
AWS & Cloud Computing Essentials
What is Amazon Web Service (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a robust cloud computing platform provided by Amazon. It provides a wide range of on-demand services, including computing power, storage, and databases, helping businesses scale and manage their IT resources efficiently.
Key Services
- EC2: Virtual servers
- S3: Scalable storage
- RDS: Managed databases
- Lambda: Serverless computing
Benefits
- Reduce infrastructure costs
- Increase flexibility
- Global deployment
- On-demand scalability
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing provides a flexible way to access IT resources online, so you pay only for what you use. Instead of investing in and managing physical data centers and servers, you can leverage technology services – such as computing power, storage, and databases – from providers such as AWS whenever you need them.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three primary categories of cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each tier offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management.
S Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides a fully managed product from the provider. With SaaS, you don’t have to worry about maintenance or managing the underlying infrastructure; your focus can be entirely on how to use the software effectively.
P Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS simplifies your operations by taking care of the underlying infrastructure so you can focus on deploying and managing your applications. No need to handle resource acquisition, capacity planning, or software maintenance.
I Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS serves as the foundational layer for cloud computing. It provides access to networking capabilities, virtual machines, and data storage solutions. You gain immense flexibility and control over your IT resources.
Ready to Leverage AWS Cloud?
Start your cloud journey with these essential services today.
The History of AWS: How Amazon Web Services Started
2004: The Beginning
Amazon introduced SQS (Simple Queue Service) in beta, marking Amazon’s first step into cloud services.
2006: Official Launch
AWS launched publicly with S3 (Simple Storage Service) and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), revolutionizing cloud infrastructure.
Expansion & Innovation
AWS introduced flagship events like Re:Invent, Storage Day, and Re:Inforce, while expanding to 200+ services across computing, storage, machine learning, and IoT.
The Pre-Cloud Challenges
Before cloud computing, businesses struggled with:
- Massive upfront investments in hardware and data centers
- Difficulty scaling to meet demand spikes
- Over-provisioning servers “just in case”
- Maintaining teams to manage physical infrastructure
Startups especially faced huge barriers to entry for basic digital services.
AWS Today
With over 200 services, AWS enables businesses of all sizes to build scalable solutions faster than ever before.
Future Growth
AWS continues growing at ~40% annually, with cloud adoption showing no signs of slowing down.
How Does AWS Work?
Global Infrastructure
AWS maintains physical data centers across multiple regions worldwide, all interconnected by a high-speed fiber network. This global infrastructure enables reliable, low-latency access to cloud services.
Regions
Geographically separate locations with multiple data centers
Availability Zones
Isolated locations within regions for fault tolerance
Edge Locations
Sites for content delivery and reduced latency
Managed Services Model
AWS handles the heavy lifting of infrastructure management, including security, maintenance, and scaling. This allows businesses to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure.
AWS Manages
- Hardware provisioning
- Security patching
- Infrastructure scaling
- Backup & recovery
You Focus On
- Application development
- Business innovation
- Customer experience
- Core competencies
Real-World Example: eCommerce Store
Running your own eCommerce store typically requires manual management of databases, including updates, security patches, scaling, backups, and failover.
Traditional vs AWS Approach
Without AWS
- Manual database management
- Time-consuming maintenance
- Complex scaling processes
- High operational overhead
With Amazon RDS
- Automated provisioning
- Managed recovery & failover
- Automatic patching
- Simplified backup
What Are the Services Provided by AWS?
AWS has a wide portfolio, offering more than 200 cloud products and services to suit different business needs. Let’s learn about some of the most sought-after AWS Services:
EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Provides a robust and flexible cloud computing solution that enhances security and scalability.
- Developers can launch applications without needing to invest in hardware upfront.
- Provides complete control over computing resources with scalable virtual servers.
Use Cases: Web hosting, application servers, development environments
S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- A powerful object storage solution known for its reliability, flexibility, and strong security measures.
- Perfect for managing data lakes, backups, and cloud-native or mobile applications.
- Provides cost-effective storage solutions with comprehensive access management.
Use Cases: Media storage, static website hosting, big data analytics
DynamoDB
- A fully managed NoSQL database that provides lightning-fast performance in just a few milliseconds.
- Allows for limitless throughput and storage, along with real-time analytics.
- Ideal for use cases like traffic pattern analysis and turning data into actionable insights.
Use Cases: Gaming leaderboards, IoT applications, high-traffic web apps
RDS (Relational Database Service)
- A relational database service that provides management for multiple database engines, such as Aurora, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB.
- Automates the management of backups, upgrades, replication, and migrations.
- Seamlessly integrates with the AWS Database Migration Service.
Use Cases: E-commerce databases, enterprise applications, content management
CloudFront
- A global Content Delivery Network (CDN) designed for rapid content delivery with minimal latency.
- Includes features like built-in compression, field-level encryption, and edge computing.
- Perfect for video streaming and high-traffic web applications.
Use Cases: Media distribution, software downloads, website acceleration
EBS (Elastic Block Store)
- Delivers robust block storage for EC2 instances, ensuring high throughput performance.
- Suitable for transactional apps and both relational and non-relational databases.
- Provides a selection of five distinct volume types designed to enhance both cost efficiency and performance.
Use Cases: Database storage, enterprise applications, boot volumes
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- A standalone cloud network that lets you customize IP ranges, subnets, and routing tables according to your needs..
- Facilitates secure public and private subnet configurations, such as web servers accessible via the internet.
Use Cases: Hybrid cloud, multi-tier applications, network isolation
Auto Scaling
- Automatically adjusts resource capacity to enhance cost efficiency.
- Compatible with EC2, Aurora, DynamoDB, and other services.
- Simplifies scaling strategies using easy-to-navigate interfaces.
Use Cases: Variable workloads, seasonal traffic, cost optimization
IAM (Identity & Access Management)
- Manages secure access to AWS resources effectively.
- Features include role-based policies, an access analyzer, and attribute-based controls.
Use Cases: Multi-user environments, compliance, least-privilege access
Cloud Directory
- A cloud-native directory service designed for multi-dimensional hierarchies.
- Scales to handle millions of objects, such as organizational charts and device registries.
- Automates the management of your infrastructure.
Use Cases: Organizational management, IoT device registries, policy stores
Key Benefits of AWS Cloud
| Benefit | Description | AWS Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Trade Capital Expenses for Variable Expenses | No upfront hardware investments | Pay-as-you-go pricing model |
| Stop Guessing Capacity | No need to predict infrastructure needs | Auto Scaling adjusts resources automatically based on demand |
| Benefit from Economies of Scale | Low cost due to the vast infrastructure of AWS | AWS passes infrastructure savings to customers |
| Eliminate Data Center Maintenance Costs | No need to manage physical infrastructure | AWS handles maintenance, updates, and hardware management |
| Increase Speed and Agility | Rapid deployment of IT resources | Provision of infrastructure in minutes |
| Go Global in Minutes | Easily deploy applications worldwide | Take advantage of AWS’s global network of data centers for low-latency access |
Why Choose AWS Cloud?
Cost Effective
High Performance
Global Reach
Secure
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud computing platform, offering a wide range of over 200 services related to computing, storage, databases, and machine learning. AWS is estimated to capture a strong 30% share of the global cloud infrastructure market by 2026, helping businesses across multiple sectors expand effectively, drive innovation, and optimize their costs.
AWS has an impressive array of customers in over 190 countries, including startups, large enterprises, academic institutions, and government agencies. Famous companies like Netflix, LinkedIn, Twitch, Paytm, Airtel, and Adobe rely on AWS to provide scalable and secure cloud solutions.
AWS provides significant cost savings and operational scaling for businesses through services such as Amazon EC2 for computing, Amazon RDS for managed databases, and Amazon Auto Scaling for dynamic resource management. A notable AWS solution by Opstree, which helped a fintech platform reduce its AWS costs by 27% while efficiently serving over 50 million users.
Some of the popular services include Amazon EC2 for computing, Amazon S3 for storage, Amazon RDS for relational databases, Amazon DynamoDB for NoSQL databases, and Amazon CloudFront for content delivery. These solutions enable businesses to deploy applications more efficiently, securely, and at scale.
Related
Author: Anshul Kichara
I’m Anshul Kichara, an SEO and Marketing Associate at Opstree Solutions, where I focus on driving digital growth through strategic content, search engine optimization, and data-driven marketing. With a passion for making technical content discoverable and impactful, I work closely with engineering teams to translate complex concepts into valuable insights for our audience. My goal is to connect innovative DevOps solutions with the people who need them—through the power of organic reach, content optimization, and smart distribution strategies. View all posts by Anshul Kichara
