In today’s DevSecOps-driven world, secrets management is not just a security best practice, it’s a necessity. Whether you’re running Kubernetes clusters, deploying microservices, or automating infrastructure, handling credentials, tokens, API keys, and certificates securely is critical. That’s where HashiCorp Vault comes in.
What is HashiCorp Vault?
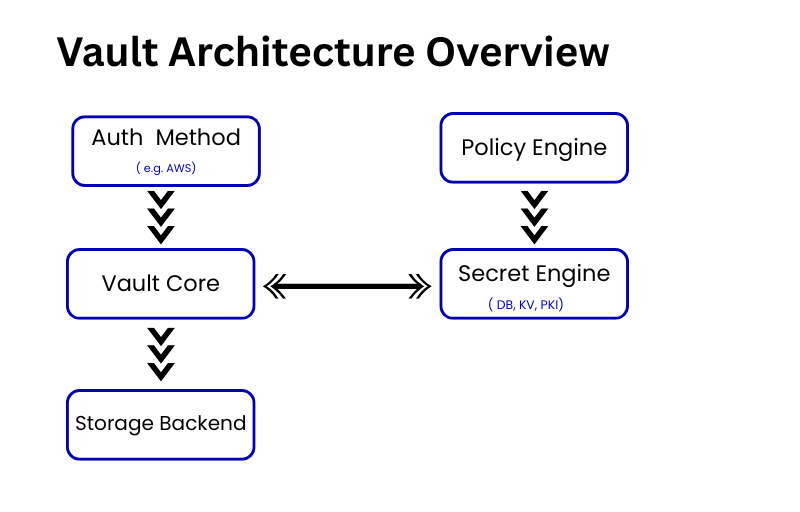
HashiCorp Vault is an open-source tool designed to secure, store, and tightly control access to secrets across distributed infrastructure. It helps you manage secrets dynamically, reduce the blast radius of breaches, and automate access control without hardcoding secrets in your apps. Vault is a cornerstone of the Zero Trust Security model where every access request must be authenticated, authorized, and encrypted.
Core Features of Vault
1. Secret Storage
Vault stores sensitive data such as API keys, passwords, and configuration settings in a centralized encrypted storage. You can store static secrets (like AWS keys) or dynamic secrets (like time-bound database credentials).
2. Dynamic Secrets
One of Vault’s most powerful features. Instead of hardcoding secrets, Vaul can generate secrets on-the-fly for databases, cloud providers, or message queues with TTLs (Time-To-Live). After the TTL expires, the credentials are revoked automatically.
3. Identity-Based Access Control (ACL)
Using Vault’s policy-based access control, you can ensure that apps, users, or systems only get access to the secrets they’re authorized for—least privilege enforced.
4. Audit Logs
Every access, request, or secret retrieval is audited, enabling traceability and compliance for standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC2.
5. Encryption-as-a-Service
Vault offers encryption/decryption APIs for developers who want to offload encryption logic without storing the data itself.
6. Pluggable Authentication
Vault supports multiple auth methods:
- GitHub
- LDAP
- Kubernetes
- AWS IAM
- Azure AD
- JWT and more
Looking for a reliable Cybersecurity Posture Management Solution?
How Does Vault Work?
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Initialize Vault: The storage backend (Consul, S3, etc.) is set up, and a master key is generated.
- Unseal Vault: Vault is locked until it’s “unsealed” using key shares (Shamir’s Secret Sharing).
- Authentication: Users/apps authenticate using a supported method (e.g., token, Kubernetes).
- Authorization: Vault checks the policies and grants access if allowed.
- Secret Retrieval/Generation: Vault returns the secret—either static or dynamically generated.
- Audit Logging: Every operation is logged securely for audit.
Common Vault Use Cases
| Use Case | Description |
| Secrets Management | Securely store and manage API keys, passwords, SSH keys, etc. |
| Dynamic DB Credentials | Rotate DB creds for MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB on-the-fly |
| PKI/Certificate Authority | Generate and manage short-lived TLS certs |
| Encryption-as-a-Service | Perform envelope encryption using Vault APIs |
| Multi-cloud Auth | Use Vault to manage identity across AWS, Azure, GCP |
| Kubernetes Secrets Injection | Inject secrets into pods securely without mounting them |
Example: Dynamic Database Credentials with Vault
Let’s say you want to generate temporary PostgreSQL credentials:
vault secrets enable database
vault write database/config/my-postgres \
plugin_name=postgresql-database-plugin \
allowed_roles="readonly" \
connection_url="postgresql://{{username}}:{{password}}@db.example.com:5432/mydb?sslmode=disable" \
username="vaultadmin" \
password="vaultpass"
vault write database/roles/readonly \
db_name=my-postgres \
creation_statements="CREATE ROLE \"{{name}}\" WITH LOGIN PASSWORD '{{password}}' VALID UNTIL '{{expiration}}'; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO \"{{name}}\";" \
default_ttl="1h" \
max_ttl="24h"
vault read database/creds/readonly
This way, apps get a unique user with limited scope, valid only for a short time.
Vault in Production: Best Practices
- Use Integrated Storage or Consul in HA mode
- Always enable audit logging
- Use TLS encryption everywhere
- Use Vault Agent + Templates for secrets injection
- Periodically rotate root/token credentials
- Leverage dynamic secrets wherever possible
- Use sentinel policies for advanced governance
Vault Deployment Options
- Self-Hosted (Open Source)
- Vault Enterprise (HA, namespaces, MFA, DR)
- HashiCorp Cloud Platform (HCP Vault)
[ Also Read: Security-as-code implementation ]
Vault vs Alternatives
| Feature | HashiCorp Vault | AWS Secrets Manager | Azure Key Vault | CyberArk |
| Open Source | ✅ Yes | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Dynamic Secrets | ✅ | ⚠️ Limited | ❌ | ⚠️ Limited |
| Multi-Cloud Support | ✅ | ❌ AWS-only | ❌ Azure-only | ✅ |
| Encryption-as-Service | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Flexible Backends | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Final Thoughts
HashiCorp Vault is more than just a password manager—it’s a modern-day secrets operating system for secure automation. If your infrastructure spans cloud, containers, and microservices, Vault ensures that secrets don’t become your weakest link. “Secrets should be dynamic, short-lived, and access-controlled—Vault helps you achieve just that.”
you can learn more about how to activate venv in vscode.
FAQs
1.What is HashiCorp Vault used for?
A. HashiCorp Vault is a secrets management tool that securely stores, manages, and controls access to sensitive data like API keys, passwords, certificates, and dynamic credentials across cloud and on-prem environments.
2.How does Vault handle dynamic secrets?
A. Vault generates short-lived, on-demand credentials (e.g., database passwords, cloud IAM roles) with a Time-To-Live (TTL), automatically revoking them after expiry to minimize exposure.
3.What authentication methods does Vault support?
A. Vault supports multiple auth methods, including Kubernetes, AWS IAM, LDAP, GitHub, Azure AD, and JWT/OIDC, enabling flexible identity-based access control.
4.How does Vault ensure security in production?
A. Best practices include enabling audit logging, using TLS encryption, deploying in High Availability (HA) mode, rotating root tokens, and leveraging dynamic secrets over static ones. 5. How is Vault different from AWS Secrets Manager or Azure Key Vault? A. Unlike cloud-native solutions (AWS/Azure-only), Vault is open-source, supports multi-cloud, offers dynamic secrets, and integrates with diverse backends (Consul, S3, etc.) for flexibility.